10 Assessment
In this chapter you will find information about:
- What is summative assessment?
- What is formative assessment?
- How does formative assessment differ from summative assessment?
- Different methods on how to use formative assessment.
What is summative assessment?
Summative assessment aims to evaluate student learning and achievement. Usually it happens at the end of a term or semester and it will compare the student’s achievement with a universal standard. Summative assessment usually has a high value, it will take place under controlled conditions (exam conditions). As summative assessment is often used as admissions (SATs, GCSEs and A-Levels) to the next educational level or the students’ results are used to list the schools by their level, it has high value and visibility.
What is formative assessment?
The goal of formative assessment is to monitor student learning to provide ongoing feedback that can be used by instructors to improve their teaching and by students to improve their learning. More specifically, formative assessments help students identify their strengths and weaknesses and target areas that need work. Formative assessments are generally low stakes, which means that they have low or no point value. Examples of formative assessments include asking students to: draw a concept map in class to represent their understanding of a topic, submit one or two sentences identifying the main point of a lecture and turn in a research proposal for early feedback. Formative assessment has the potential to refocus students on the learning process and its intrinsic value, encourage students to build on their strengths, help students become more aware of their learning needs, strengths, and interests so they can take greater responsibility over their own educational growth. For example, students may learn how to self-assess their own progress and self-regulate their behaviours.
Formative assessment and summative assessment are two overlapping, complementary ways of assessing pupil progress in schools. While the common goal is to establish the development, strengths and weaknesses of each student, each assessment type provides different insights and actions for educators. The key to holistic assessment practice is to understand what each method contributes to the end goals.
Methods for formative assessment:
-
- Entry and exit slips – Start the class with a question about the previous work. You can ask different questions yourself or you can let students discuss in groups what they have learned. For example the question can be: “What are the two things you learned today? What did you find interesting in today’s class?” At the end of the lesson you can use good old pencil and paper or you can choose to use different technology like Padlet or any Poll tool to measure the progress and if they are in the middle of some bigger task to write down where they stopped with their ideas and progress.
- Questions that teachers pose to individual students and groups of students during the learning process to determine what specific concepts or skills they may be having trouble with. A wide variety of intentional questioning strategies may be employed, such as phrasing questions in specific ways to elicit more useful responses.
- Methods that help students to express their understanding of the topic in another way. For example let students write a letter explaining a key idea to a friend, draw a sketch to visually represent new knowledge, or do a think, pair, share exercise with a partner.
- Interview assessments. Try discussion-based assessment methods if you want to dig deeper into students’ understandings.
- Art methods. Let students draw, create a collage, create a videna, dance or a play. All these methods help students to act out their understanding of the content.
- Peer assessments that allow students to use one another as learning resources. For example, “workshopping” a piece of writing with classmates is one common form of peer assessment, particularly if students follow a rubric or guidelines provided by a teacher.
- Self-assessment. Let students spot their strengths and weaknesses themselves by giving them your rubric to follow. For quick insight you can project the rubric on the class wall and let students mark with sticky-notes their progress. For more information about different formative assessment read Natalie Regier’s 60 methods for Formative assessment.
Exercise to help to find out what type of formative assessment to use:
Think about the following questions:
1) What aspects of student learning would you like to measure?
2) What are the learning preferences of the students?
3) What other methods are you using (the methods could be connected or support each other)
4) Should you use individual strategy or group strategy? (You should use both if possible, if there are struggling students they might need more individual strategies)
5) How to use the information you got from the use of the strategy? (Should you rethink the lesson design and methods? )
Useful tools for teachers
Checklists — Class checklists are a great tool for collecting data about students during a unit of study or a project based learning (Figure 1).
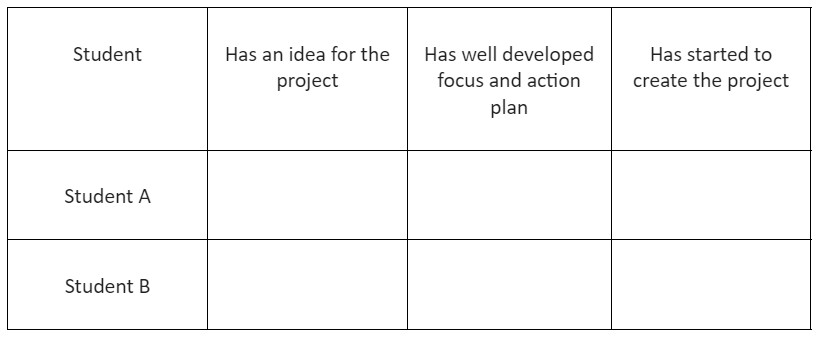
Figure 1. Checklist example for project based learning assessment
Rubrics – Creating formative assessment rubrics is based on the idea that learning goals are continuous. Starting from the easiest goals and developing to more complex ones. Creating rubrics and sharing them with students helps to better understand their development and make them more self aware about their learning. It will also let students know how far they can develop their knowledge. When creating a rubric it is important to to keep in mind that the descriptions need to be in increasing sophistication order. The following picture (Figure X) is an example of how rubrics can be used to evaluate students progress on a project based learning activity. There are numerous online rubric creating tools that can be used to simplify the process, for example https://rubric-maker.com/.
Reflection
Use the note box and reflect on the following questions:
- Think about the concept of STEAM. What methods do you see for implementing this methodology as:
a) the possibility
b) the challenge
c) the risk
2. Answer to these essential question:
a) Where would you take advantage of the new opportunities?
b) How would you meet the challenge?
c) What ways would you choose to manage the risk?
